
What is an induction hob and how do they work?
An induction hob consists of a copper coil beneath a ceramic or glass surface, powered by electricity. It requires induction-compatible cookware with a ferrous base like stainless steel or cast iron. When a cooking zone is activated, the coil generates a rapidly changing magnetic field that induces an electric current in the cookware's base, producing heat through electrical resistance. Precise temperature control is achieved instantly, and the hob's surface remains relatively cool for safety. The control panel allows users to adjust settings, making induction hobs efficient and user-friendly.
How does an induction hob work
An induction hob operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction to heat cookware directly, without using traditional heating elements like gas flames or electric coils. Instead, an induction hob generates an alternating magnetic field beneath its glass or ceramic surface. When you place a compatible ferrous (iron-containing) cookware, such as stainless steel or cast iron, onto the surface, the magnetic field induces an electric current within the cookware, creating heat.
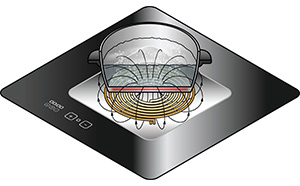
This process is highly efficient, allowing for precise temperature control and rapid heating while maintaining the cooktop's surface cool to the touch, making it safer and more energy-efficient than conventional stoves. Induction hobs have become increasingly popular for their speed, responsiveness, and energy-saving capabilities, making them a favourite choice for professional chefs and home cooks alike.
What is electrical induction?
Electrical induction, often referred to as magnetic induction, is the generation of voltage within a conductor as a result of its interaction with a magnetic field. This phenomenon underscores the essential relationship between magnetic fields and induced electrical currents.
An induction hob functions through electromagnetic induction, where a coil of copper wire beneath the hob's surface generates an alternating magnetic field when powered. When ferrous cookware, such as stainless steel or cast iron, is positioned on the hob, this changing magnetic field induces an electric current within the cookware, resulting in resistance and rapid heating. Subsequently, the cookware transfers this heat to the food or liquid inside, allowing for precise and efficient cooking. Importantly, induction hobs offer safety advantages with their cool surface and instant heat control, making them a favoured choice in many UK kitchens.
Safety of induction hobs and pacemakers
Induction hobs are equipped with various safety features, including automatic shut-off when no cookware is detected, pan detection to ensure compatibility, child lock functions, residual heat indicators, and overheat protection, all designed to enhance safety during cooking. Regarding pacemakers, induction hobs typically generate enclosed electromagnetic fields that pose minimal risk to pacemakers or medical devices. However, individuals with such devices should consult their healthcare provider or device manufacturer for specific guidance on electromagnetic interference and should consider maintaining a safe distance from the hob when in use, even though the risk is generally low.

What makes induction cooking different from electric and gas?
Induction cooking distinguishes itself from electric and gas methods by directly heating cookware through electromagnetic induction, requiring compatible ferrous-based pots and pans. It excels in speed, precision, and energy efficiency, heating rapidly with instant temperature adjustments while keeping its surface cool for safety. Electric stovetops, while slower to heat and less responsive, use electric coils.
Induction, ceramic or gas - which is best?
Selecting the optimum hob—be it induction, ceramic, or gas—comes down to your particular cooking requirements and personal preferences. Induction hobs excel in speed, precision, and energy efficiency, making them an ideal choice for those valuing rapid heating and safety. Ceramic hobs, on the other hand, offer versatility, comfortably handling various cooking tasks with simplicity. Meanwhile, gas hobs provide the traditional appeal of open flames, offering high heat and precise control but demanding extra attention to safety and energy efficiency. Your ultimate decision hinges on factors such as your cooking style, safety concerns, and energy efficiency priorities.

In this comparison, we'll explore the strengths of each hob type across various cooking scenarios. Whether you're an experienced chef or a home cook searching for the perfect kitchen companion, this guide will assist you in making an informed choice.
| Cooking Scenario | Gas Hob | Induction Hob | Ceramic Hob |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boiling Water | Good for rapid boiling; instant heat | Excellent for rapid heating; precise temperature control | Adequate for boiling |
| Frying | Ideal for frying with even heat distribution | Excellent for precise temperature control; instant response | Suitable for frying |
| Simmering | Good for simmering with low heat settings | Excellent for precise and consistent simmering | Suitable for simmering |
| Stir-frying | Good for stir-frying with high heat | Excellent for stir-frying; instant response and precise control | Adequate for stir-frying |
In summary, the choice between gas, induction, or ceramic hobs depends on your cooking preferences and requirements. Gas hobs excel in rapid boiling and stir-frying, offering precise control, while induction hobs are ideal for those seeking rapid heating and precision across various cooking techniques. Ceramic hobs are versatile and suitable for general cooking tasks. Understanding their strengths in different scenarios will help you select the hob that complements your culinary style and kitchen requirements.
